Anthropometry & Ergonomics for Comfort & Functionality
Interior design is not just about aesthetics—it’s about human comfort, efficiency, and usability. Anthropometry and ergonomics are two crucial principles that help designers create spaces that fit people’s needs while promoting well-being and functionality.
Let’s dive into how these concepts impact interior design and why they are essential for every designer.
1. What is Anthropometry?
Anthropometry is the study of human body measurements and how they relate to furniture, layouts, and space planning.
Why is Anthropometry Important?
✔️ Prevents furniture that is too high, too low, or too deep for comfort.
✔️ Ensures that walkways and spaces accommodate different body sizes.
✔️ Helps create ergonomically optimized designs that reduce discomfort.
📏 Standard Anthropometric Guidelines in Interior Design:
- Seating Height: 16-18 inches from the floor.
- Dining Table Height: 28-30 inches.
- Kitchen Counter Height: 36 inches for comfortable use.
- Desk Height: 28-30 inches for proper posture.
- Bed Height: 22-25 inches for ease of getting in and out.
📌 Pro Tip: Consider regional and demographic variations in anthropometric data to design for different populations.

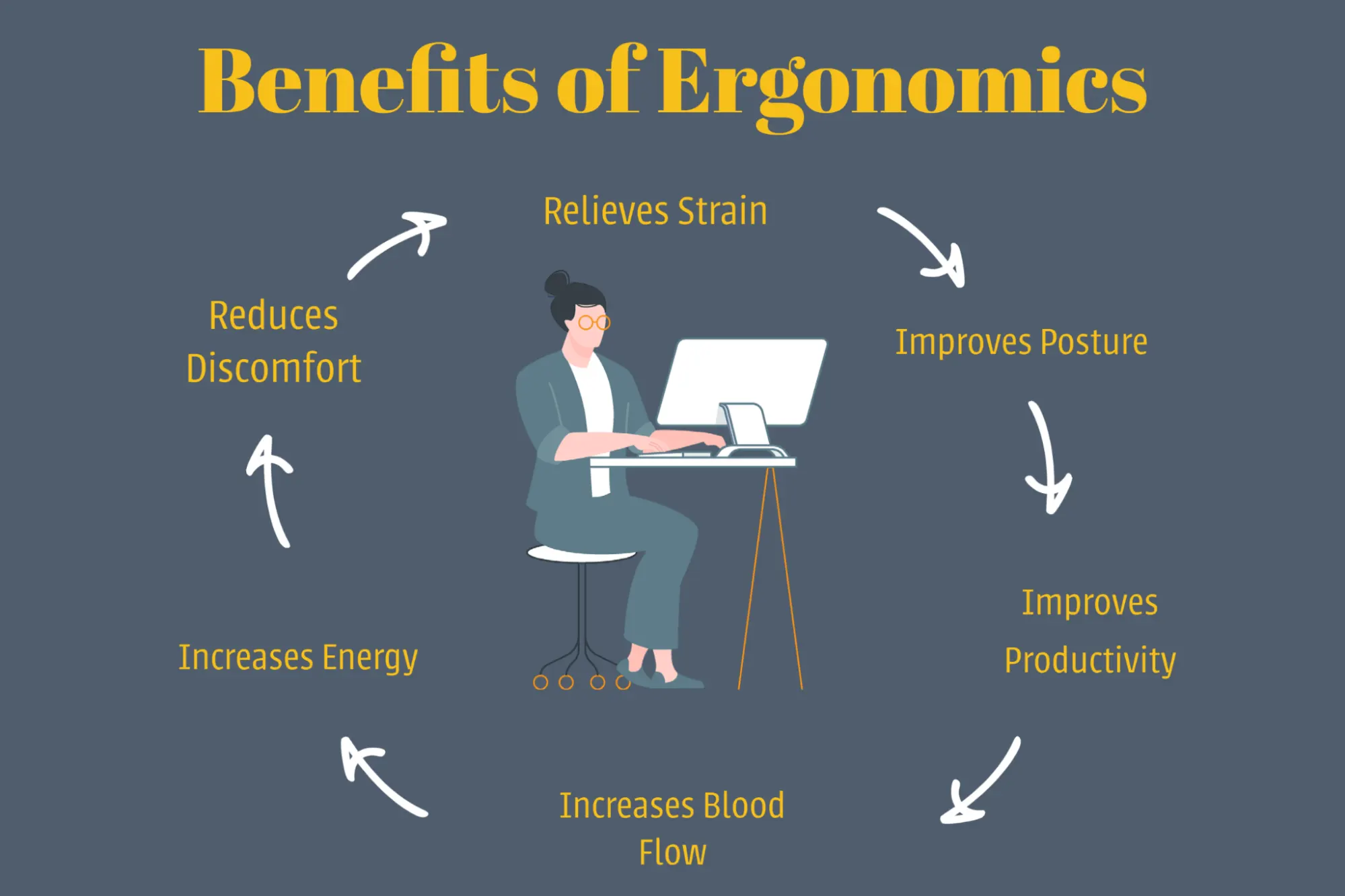
2. What is Ergonomics?
Ergonomics is the science of designing furniture, tools, and spaces for human efficiency, safety, and comfort. It ensures that users experience minimal strain and maximum ease while interacting with their environment.
🔹 Key Ergonomic Factors in Interior Design:
✔️ Posture Support: Chairs and sofas should promote a natural spinal curve.
✔️ Visual Comfort: Workspaces should be designed to prevent eye strain and glare.
✔️ Movement & Accessibility: Spaces should allow for effortless reach and mobility.
✔️ Safety & Ease of Use: Avoid sharp corners and difficult-to-reach storage spaces.
📌 Pro Tip: In workspaces, an ergonomic desk-chair setup prevents back pain and boosts productivity.
3. Applying Anthropometry & Ergonomics in Design
🔹 Living Rooms: Ensure furniture dimensions accommodate different postures while maintaining comfort.
🔹 Workspaces: Use adjustable seating and correct screen heights to reduce strain.
🔹 Kitchens: Counters should be customized for the user’s height to minimize back discomfort.
🔹 Bathrooms: Sinks and vanities should be positioned at an optimal height to prevent awkward bending.
📌 Pro Tip: Use adjustable and modular furniture to cater to different user preferences.
Final Thoughts
By incorporating anthropometry and ergonomics, interior designers create comfortable, efficient, and user-friendlyspaces. Ignoring these principles leads to discomfort, inefficiency, and even health issues.
Understanding how people interact with their environment is the key to great design!
What are your thoughts on designing for comfort and functionality? Let’s discuss in the comments! 👇✨
